How the body processes carbohydrates
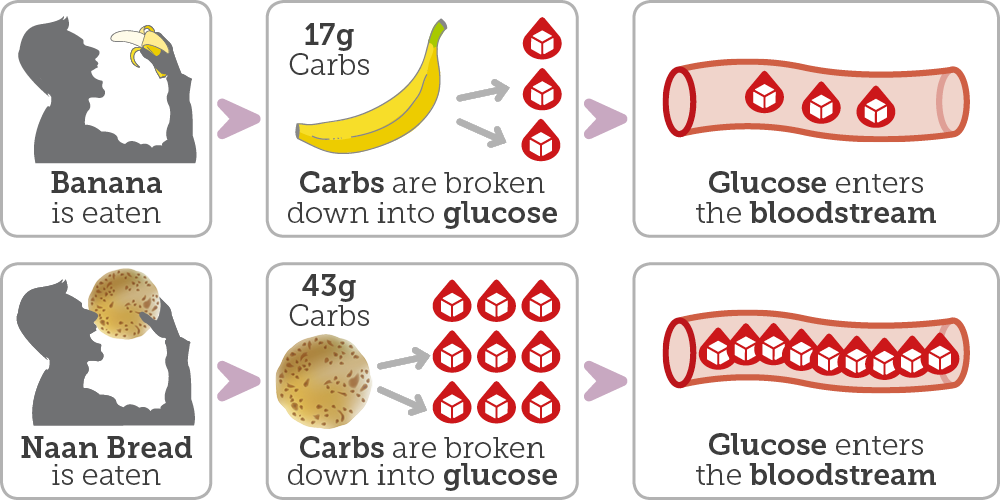
All carbohydrates are broken down to glucose (sugar) in the body, which then enters our bloodstream and is used by the cells in our body as a source of energy.
Carbohydrate is the nutrient that will have the biggest impact on our blood glucose levels. The type and portion size of carbohydrate will also affect blood glucose levels.
Types of carbohydrate
With starchy carbohydrates, it is better to opt for wholegrain options such as brown rice, pasta or wholegrain bread, where possible as they contain more of the vitamins and minerals from the original cereal grain.
Wholegrain foods take longer for our body to digest. They release glucose into the blood much slower than sugary foods and drinks. They can help stabilise blood glucose levels and also keep you feeling fuller for longer.
Refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, pasta and rice are highly processed. This means that much of the grain has been removed to give a ‘whiter’ effect.
The result is that these foods are broken down to glucose much faster by the body so you get a sharp spike in your blood glucose levels, followed by a crash which can leave you craving more high-carb foods.
Portion sizes
Along with the type of carbohydrate, the amount of carbohydrate you are eating also impacts blood glucose levels. Have a look at the diagram below showing the effects of different portions of white rice on glucose levels:
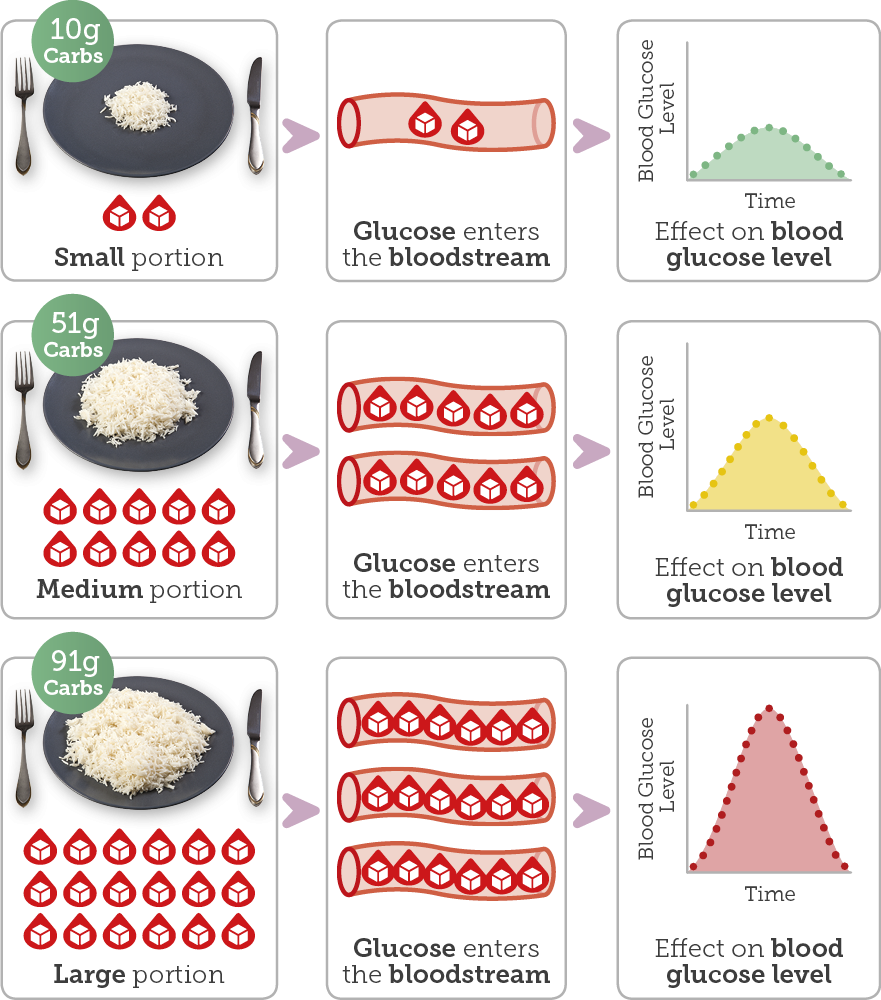
As you can see a large portion of rice releases a lot more glucose into the bloodstream and it results in a bigger sugar crash compared to a smaller portion.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.