Diabetes explained
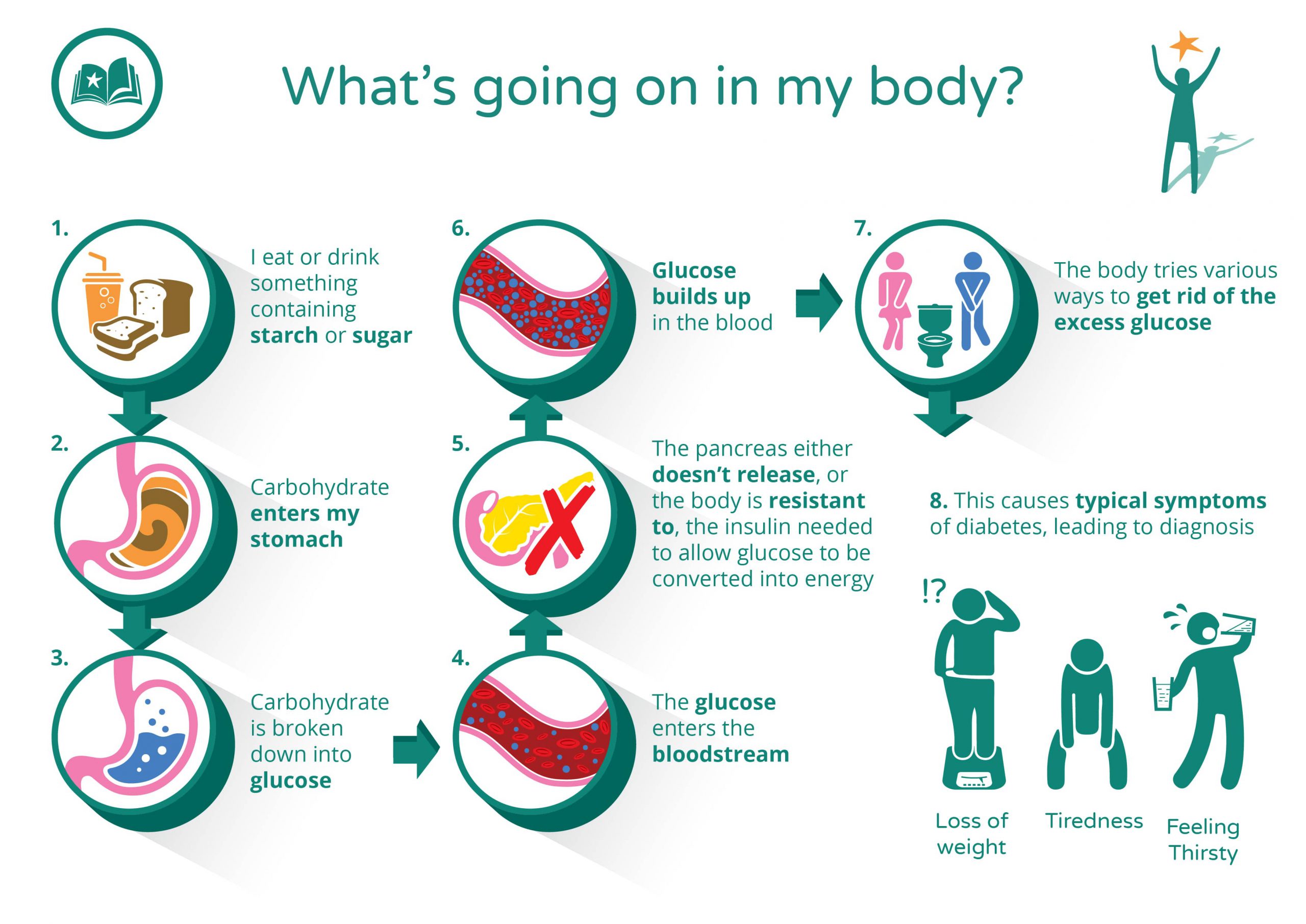
Diabetes is a condition where someone has too much glucose – a type of sugar – in their blood. When people don’t have diabetes their blood glucose levels are controlled by a hormone called insulin that is produced in their pancreas.
If someone has diabetes, they’re either not producing insulin, or the insulin they do produce can’t work properly or there isn’t enough of it. This means that glucose builds up in their blood and can’t get into the cells of their body where it’s used for fuel. If the condition is untreated and there is continuously too much glucose in the blood, this can lead to long term complications including sight loss, amputation, kidney failure, stroke and death.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes develops when the body still makes some insulin but it’s not able to work properly or there isn’t enough. Some people can manage it with a healthy diet, regular physical activity and, if they need to, by losing weight. But the longer someone has type 2, the more likely it is that they will need medication. About a quarter of people with type 2 will eventually need to take insulin.
About 90% of people that have diabetes have type 2 and in about 3 in 5 cases, type 2 can be prevented or at least delayed by making healthier food and lifestyle choices.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.