What is type 1 diabetes?
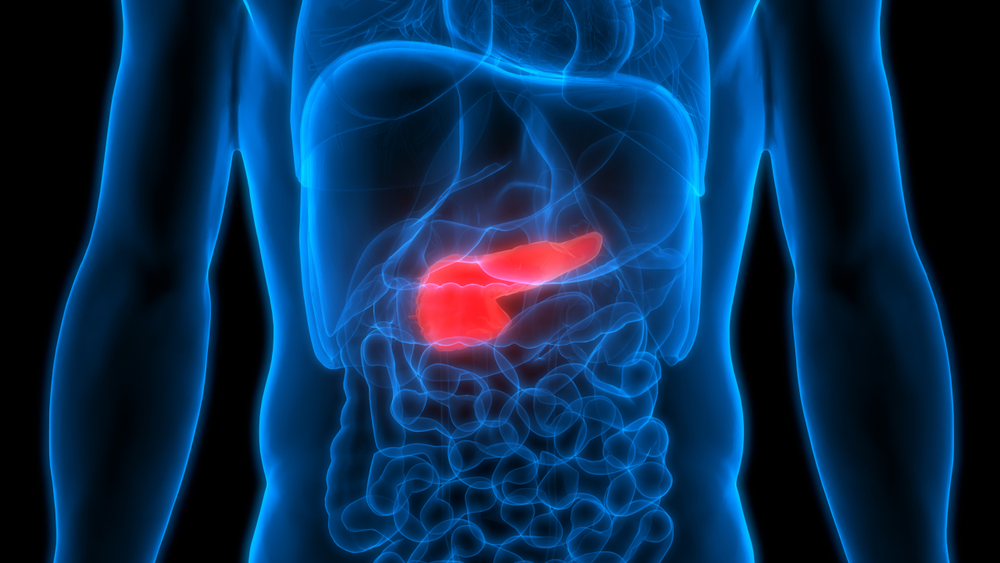
To understand what causes diabetes, you first need to understand what your pancreas is and what it does.
The pancreas is a gland that sits behind your stomach and plays a part in the digestive process. The pancreas releases a substance (hormone) called insulin when it senses a rise in your blood glucose levels (usually after you eat or drink). The insulin allows the glucose to enter the cells of your body and be converted into energy.
People develop type 1 diabetes when the insulin-producing cells in their pancreas, called beta cells, are destroyed by other cells, called immune cells. These immune cells see the beta cells as a threat to the body. This is known as an autoimmune process. Without the beta cells, insulin cannot be produced. The cause of this autoimmune process is not fully understood. There is sometimes a genetic cause (which means it can be passed down through your family), but this is not always the case. It is thought that other factors, such as viral infections, may also be responsible for some people developing type 1 diabetes.
What is going on in my body?
The following diagram explains what goes on in your body when you have undiagnosed or untreated diabetes. You may not be familiar with all these terms and concepts just yet, but you will learn much more about them as you work through the course.
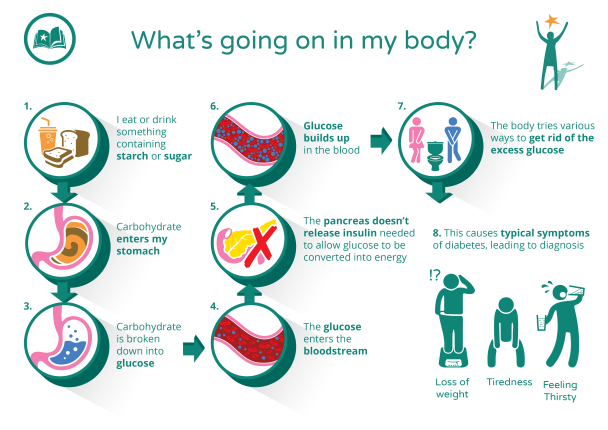
What is blood glucose and why is it important?
Blood glucose is the sugar that our bodies make when we eat food containing carbohydrates. Carbohydrates (often called carbs) are found in starchy foods, such as bread, pasta, rice and potatoes, and sugary foods such as sweets, cakes, fruit juices and biscuits.



Your body converts the sugars in these foods to glucose. When glucose enters the cells of your body, it is converted into energy. You then use this energy to feed your cells and carry out your daily activities. Glucose also helps with the growth and cell repair inside your body and helps your brain and other important organs to work properly.
When you increase your activity levels, for example when you exercise, you need more glucose for energy.
What happens when my body does not make insulin?
When you have not enough insulin in your body, the glucose from your food or drink cannot enter your cells to be converted into energy. This causes a build-up of glucose in the blood, which is called hyperglycaemia. The body tries to compensate and get rid of the excess glucose in the urine. Your body will also release any glucose stored in your liver and muscles and then break down the fat in your body, to use that for energy instead.
I’ve heard something about ketones. What are they?
If your body does not have enough insulin, it cannot use glucose from your blood as energy and it will instead begin to burn fat. When this happens, a harmful substance called ketones is produced. If you do not have enough insulin on board to enable your body to get rid of the excess ketones, it can cause a dangerous condition called diabetic ketoacidosis.
What is diabetic ketoacidosis?
Ketones are acidic and if not cleared can change the chemical balance of the blood. This is called diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA, and can be very dangerous. DKA can cause stomach pains, vomiting and diarrhoea, and blood glucose levels are usually persistently high. The body tries to get rid of the ketones by producing more urine. As a result, the body loses lots of water, resulting in severe dehydration. DKA needs urgent hospital treatment with fluid and insulin, otherwise dehydration from DKA can be fatal.
Do I have any beta cells left in my pancreas?
For the first five years after you are diagnosed with diabetes, your pancreas may still have some beta cells that produce insulin. This is known as the honeymoon period. You will learn more about this later in the course.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.